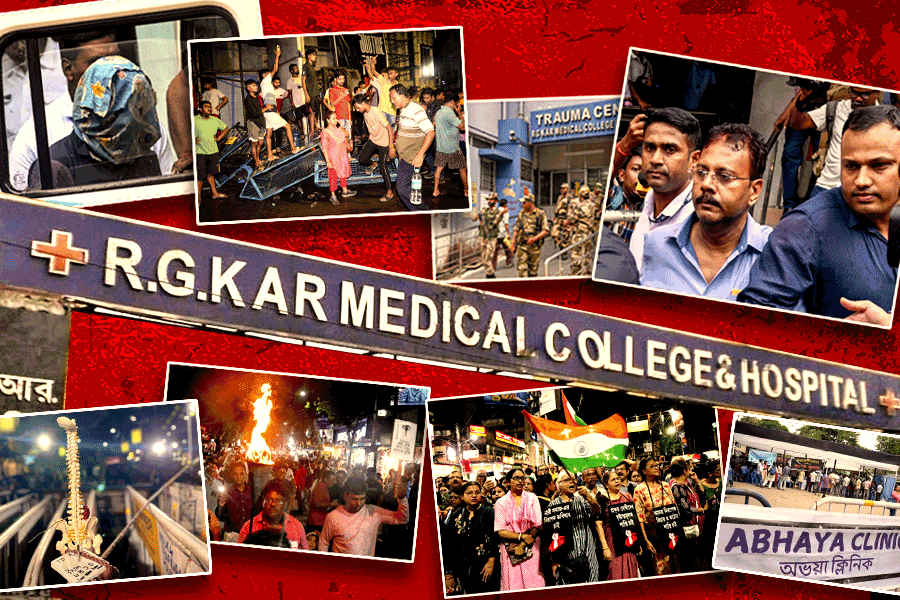The Indian Initial Public Offering (IPO) market has witnessed a surge in activity in recent years, with companies across diverse sectors seeking to tap into public capital. While there might be shares listing at a premium, there are also shares listing on discount.
Recently, a recurring phenomenon observed in many IPOs is underpricing, where the offer price of shares is set below their true market value. This practice of underpricing often leads to a significant jump in share prices on the listing day, leaving investors wondering why companies deliberately leave money on the table. Let us learn about the intricacies of IPO pricing strategies and what is delivery trading, shedding light on the rationale behind underpricing and its implications for Indian investors.
The Dynamics Of IPO Pricing
Determining the "right" price for an IPO is a complex exercise involving a delicate balance of factors. Companies aim to raise sufficient capital while ensuring that the offering is attractive to investors. Investment banks, acting as underwriters, play a crucial role in this process, conducting due diligence, assessing market demand, and advising on the appropriate price range.
The Balancing Act
Raising Sufficient Capital
The primary goal of an IPO is to raise funds for the company. This means setting a price that attracts enough investors to purchase the desired number of shares. An excessively low price might leave money on the table, while an excessively high price could lead to an undersubscribed IPO.
Attracting Investors
The IPO needs to be appealing to investors. This means offering shares at a price that they perceive as fair, or even slightly undervalued, giving them the potential for future gains. Investors consider factors like the company's growth prospects, financial health, industry trends, and overall market conditions.
The Role Of Investment Banks (Underwriters)
Investment banks act as intermediaries between the company and the investors. They play a multifaceted role in the IPO pricing process:
Due Diligence
They conduct extensive research on the company, analysing its financial statements, business model, competitive landscape, and management team to assess its value and potential.
Market Assessment
They gauge investor sentiment and market demand for the company's shares through roadshows, investor meetings, and market analysis. This helps them understand the price range that investors might be willing to accept.
Valuation
They employ various valuation techniques, such as discounted cash flow analysis, comparable company analysis, and precedent transaction analysis, to arrive at a fair estimate of the company's worth.
Pricing Recommendation
Based on their due diligence, market assessment, and valuation analysis, they advise the company on an appropriate price range for the IPO. This involves considering factors like the company's financial performance, growth prospects, industry comparables, and overall market conditions.
The Delicate Balance
The "right" IPO price is not an exact science. It's a delicate balancing act between the company's need to raise capital and the investors' desire for a fair price. Underwriters play a crucial role in navigating this complexity, using their expertise and market knowledge to arrive at a price that satisfies both parties.
Below are the factors influencing the final price of an IPO:
Company's financial performance and growth prospects
Industry trends and competitive landscape
Overall market conditions and investor sentiment
The company's desired valuation and fundraising goals
The level of risk associated with the investment
Ultimately, the IPO pricing process is a collaborative effort between the company, its underwriters, and potential investors. When you open free demat account and check an IPO price, these are the steps it has gone through.
Reasons For Underpricing
Several factors contribute to the prevalence of underpricing in IPOs:
Information Asymmetry
Companies and their underwriters often possess more information about the company's prospects than potential investors. Underpricing can compensate investors for this information gap and incentivize them to participate in the offering.
Creating a "Buzz"
A successful IPO with a strong first-day performance generates positive publicity and attracts further investor interest. Underpricing can create a "buzz" around the offering, increasing demand and ensuring a smooth listing.
Mitigating Risk
Underpricing reduces the risk of the IPO being undersubscribed. By setting a lower price, companies can attract a wider range of investors and ensure sufficient demand for the shares.
Rewarding Early Investors
Underpricing can be seen as a way to reward early investors who have supported the company in its initial stages. A significant first-day gain can generate substantial returns for these investors, fostering goodwill and encouraging future investments.
Signalling Optimism
Underpricing can signal confidence in the company's future prospects. By leaving money on the table, companies convey a belief that the shares are undervalued and have significant upside potential.
Check an investment app for undervalued stocks and new IPO launches.
Implications For Indian Investors
While underpricing can benefit investors by providing an opportunity for listing gains, it is essential to approach IPOs with a cautious and informed perspective:
Avoid Chasing Hype
Avoid getting caught up in the hype surrounding an IPO. Conduct thorough research on the company's fundamentals, financials, and growth prospects before investing.
Long-term Perspective
Focus on the company's long-term potential rather than short-term listing gains. Evaluate the company's business model, competitive landscape, and management team to assess its sustainability.
Diversification
Diversify your investment portfolio across different sectors and asset classes. Don't allocate a disproportionate amount of capital to IPOs, especially in volatile market conditions.
Risk Assessment
Understand the risks associated with IPO investments. New companies may face challenges in scaling their operations and achieving profitability.
Regulatory Measures
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has implemented measures to address concerns related to IPO pricing and protect investor interests. These include the following:
Enhanced Disclosures
Companies are required to provide comprehensive disclosures in their offer documents, including detailed financial information, risk factors, and management profiles.
Price Bands
SEBI mandates the use of price bands in IPOs, providing a range within which the final offer price can be determined. This promotes transparency and allows for market-driven price discovery.
Monitoring And Surveillance
SEBI closely monitors IPO activity and takes action against any manipulative practices or misrepresentations.
Conclusion
Underpricing in IPOs is a complex phenomenon driven by a combination of factors. While it can create opportunities for investors, it's crucial to approach IPOs with a balanced perspective, conducting thorough research and understanding the associated risks. SEBI's regulatory measures aim to promote transparency and protect investor interests in the evolving IPO landscape. By downloading a stock market app, staying informed and adopting a prudent investment strategy, Indian investors can navigate the complexities of the IPO market and make informed decisions aligned with their financial goals.
This is a PR article which has been published as received without any editorial enhancement, or modification.. The Telegraph Online does not endorse or guarantee the accuracy, reliability, or completeness of any information presented in the article. The organization is not responsible for any errors or omissions in the content or for any losses, damages, or injuries arising from the use of the information provided in the article.
'