A 7.1-magnitude earthquake rattled Southern California on Friday night, one day after the strongest recorded quake there in 20 years struck — and seismologists warned that further episodes are expected.
The US Geological Survey reported that the latest earthquake’s epicentre was in the Mojave Desert, 11 miles from Ridgecrest, California — near where a 6.4-magnitude quake had hit about 36 hours earlier.
Since Thursday’s earthquake, the area had been jolted by a series of rolling aftershocks, including one of a 5.4-magnitude that roused Californians on Friday morning.
“Hold on, it’s going again,” Jade Alexander, the manager of the Rodeway Inn & Suites in Ridgecrest, said in a phone interview following another aftershock on Friday night. She said the aftershocks were coming every five minutes.
Although the area where the earthquake struck is sparsely populated, the navy has a weapons testing facility just outside Ridgecrest, the Naval Air Weapons Station China Lake.
“It’s constant,” said Alexander, whose hotel in Ridgecrest is less than a five-minute drive from the naval station. “My anxiety level is over the limit.”
“The floor is cracked,” she added, saying that bookshelves, lockers and televisions were thrown to the ground.
The quake, which struck at about 8.20pm (local time), was felt across a much wider area than Thursday’s, with reports of power failures in Los Angeles, and of some damage in San Bernardino county. It was also felt in Las Vegas, though the Nevada Highway Patrol had received no reports of damage to roads or bridges.
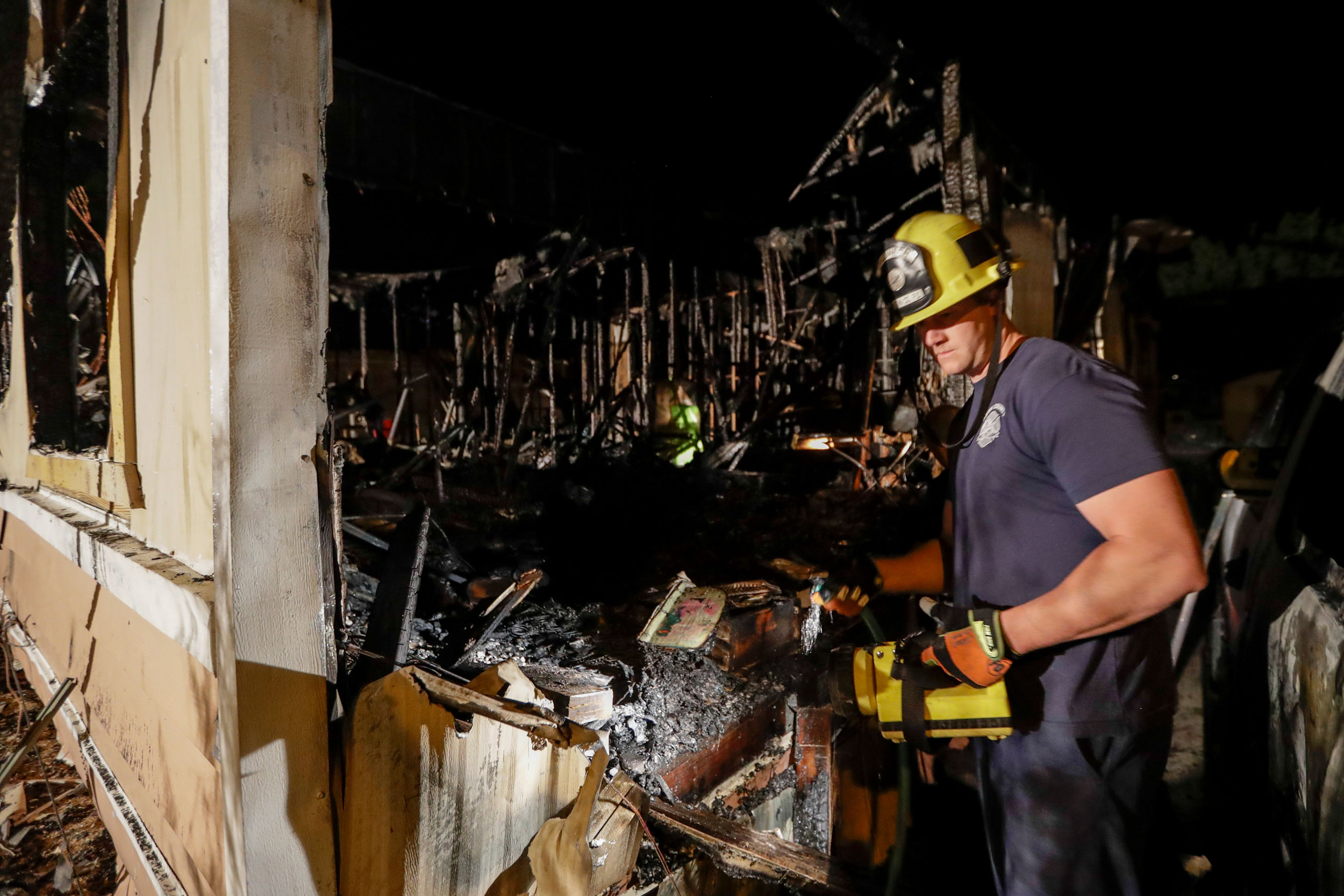
Mick Gleason, the supervisor of Kern county, which includes Ridgecrest, said that some people had been injured but that no deaths had been reported. There were at least two fires, including one at a mobile home park, he told CNN. One big concern was gas leaks.
Kern County Fire Chief David Witt said that it appeared that no buildings had collapsed.
Lucy Jones, a seismologist, said during a Friday night briefing by the US Geological survey that there would be more aftershocks. “It is clearly an energetic system,” Jones said.
At 8.21pm (local time), the Los Angeles Fire Department issued an earthquake alert from its Twitter account.
“Prepare For Aftershocks,” the tweet said. “When Shaking Starts: DROP, COVER, HOLD ON!”
In Los Angeles, fire officials reported localised power failures and wires down in several city neighbourhoods, but said that no major damage to infrastructure had been identified.
In San Bernardino county, fire officials said that there was more damage from the Friday night earthquake than there was from the one the day before. The officials reported that homes had been shifted, foundations had been cracked and retaining walls had collapsed.
Tom Heaton, an earthquake expert at the California Institute of Technology, said the earthquake Friday night appeared to have taken place northwest of Thursday’s earthquake. The rupture was about 10 to 15 miles long, and the duration of the earthquake was around seven seconds.
Friday’s earthquake was much larger than Thursday’s; the total energy released was about eight times greater.
For now the earthquakes appear to be localised. There is “no plausible connection” between these earthquakes and the San Andreas, the larger and potentially more destructive fault that runs from the Gulf of California to well north of San Francisco, Heaton said.
“But in this business I don’t like to ever say things can never happen,” Heaton said.
The region where both Thursday’s and Friday’s earthquakes struck is characterised by a complex set of faults that have helped form geological features called basins and ranges.
“I like to tell people that earthquakes are very social in the basin and range; they don’t like being alone,” Dr. Heaton said. “I would be surprised if this thing just stopped.”
The largest known earthquake in the area occurred in 1872 and was a magnitude 8, one of the largest in California.