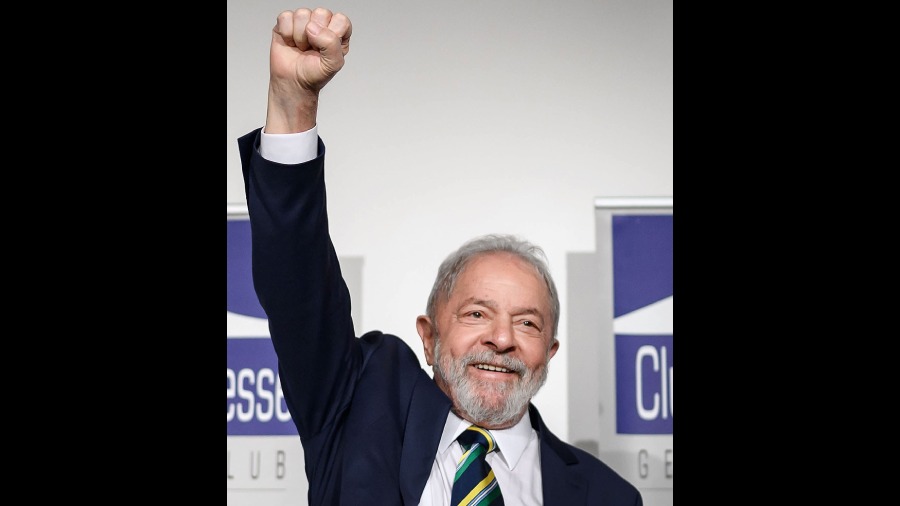
Luiz In cio Lula da Silva has done it again: Twenty years after first winning the Brazilian presidency, the leftist defeated incumbent Jair Bolsonaro Sunday in an extremely tight election that marks an about-face for the country after four years of far-right politics.
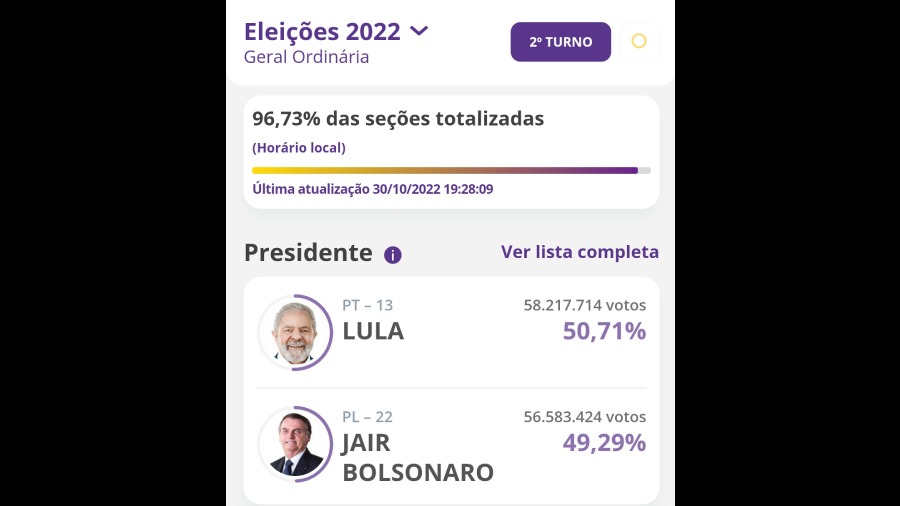
With more than 99 per cent of the votes tallied in the runoff vote, da Silva had 50.9 per cent and Bolsonaro 49.1 per cent, and the election authority said da Silva's victory was a mathematical certainty.
Twitter @Vinncent
It is a stunning reversal for da Silva, 77, whose 2018 imprisonment over a corruption scandal sidelined him from the 2018 election that brought Bolsonaro, a defender of conservative social values, to power.
"Today the only winner is the Brazilian people," da Silva said in a speech at a hotel in downtown Sao Paulo. "This isn't a victory of mine or the Workers' Party, nor the parties that supported me in campaign. It's the victory of a democratic movement that formed above political parties, personal interests and ideologies so that democracy came out victorious."
Da Silva is promising to govern beyond his leftist Workers's Party. He wants to bring in centrists and even some leaning to the right who voted for him for the first time, and to restore the country's more prosperous past. Yet he faces headwinds in a politically polarised society where economic growth is slowing and inflation is soaring.
His victory marks the first time since Brazil's 1985 return to democracy that the sitting president has failed to win reelection. The highly polarised election in Latin America's biggest economy extended a wave of recent leftist victories in the region, including Chile, Colombia and Argentina.
As Lula spoke to his supporters promising to "govern a country in a very difficult situation" Bolsonaro had yet to concede the election.
It was the country's closest election in over three decades. Just over 2 million votes separated the two candidates with 99.5 per cent of the vote counted. The previous closest race, in 2014, was decided by a margin of 3.46 million votes.
Da Silva's inauguration is scheduled to take place on January 1. He last served as president from 2003-2010.
Thomas Traumann, an independent political analyst, compared the results to Biden's 2020 victory, saying da Silva is inheriting an extremely divided nation.
"The huge challenge that Lula has will be to pacify the country," he said. "People are not only polarised on political matters, but also have different values, identity and opinions. What's more, they don't care what the other side's values, identities and opinions are."
Congratulations for Lula and Brazil began to pour in from around the world Sunday evening, including from US President Joe Biden, who highlighted the country's "free, fair, and credible elections." The European Union also congratulated da Silva in a statement, commending the electoral authority for its effectiveness and transparency throughout the campaign.
Bolsonaro had been leading throughout the first half of the count and, as soon as da Silva overtook him, cars in the streets of downtown Sao Paulo began honking their horns. People in the streets of Rio de Janeiro's Ipanema neighbourhood could be heard shouting, "It turned!"
Da Silva's headquarters in downtown Sao Paulo hotel only erupted once the final result was announced, underscoring the tension that was a hallmark of this race.
"Four years waiting for this," said Gabriela Souto, one of the few supporters allowed in due to heavy security.
Outside Bolsonaro's home in Rio de Janeiro, ground-zero for his support base, a woman atop a truck delivered a prayer over a speaker, then sang excitedly, trying to generate some energy. But supporters decked out in the green and yellow of the flag barely responded. Many perked up when the national anthem played, singing along loudly with hands over their hearts.
Most opinion polls before the election gave a lead to da Silva, universally known as Lula, though political analysts agreed the race grew increasingly tight in recent weeks.
For months, it appeared that da Silva was headed for easy victory as he kindled nostalgia for his presidency, when Brazil's economy was booming and welfare helped tens of millions join the middle class.
But while da Silva topped the October 2 first-round elections with 48 per cent of the vote, Bolsonaro was a strong second at 43 per cent, showing opinion polls significantly underestimated his popularity. Many Brazilians support Bolsonaro's defence of conservative social values and he shored up support in an election year with vast government spending.
Bolsonaro's administration has been marked by incendiary speech, his testing of democratic institutions, his widely criticised handling of the COVID-19 pandemic and the worst deforestation in the Amazon rainforest in 15 years. But he built a devoted base by defending conservative values and presenting himself as protection from leftist policies that he says infringe on personal liberties and produce economic turmoil.
Da Silva is credited with building an extensive social welfare programme during his 2003-2010 tenure that helped lift tens of millions into the middle class as well as presiding over an economic boom. The man universally known as Lula left office with an approval rating above 80 per cent; then U.S. President Barack Obama called him "the most popular politician on Earth."











