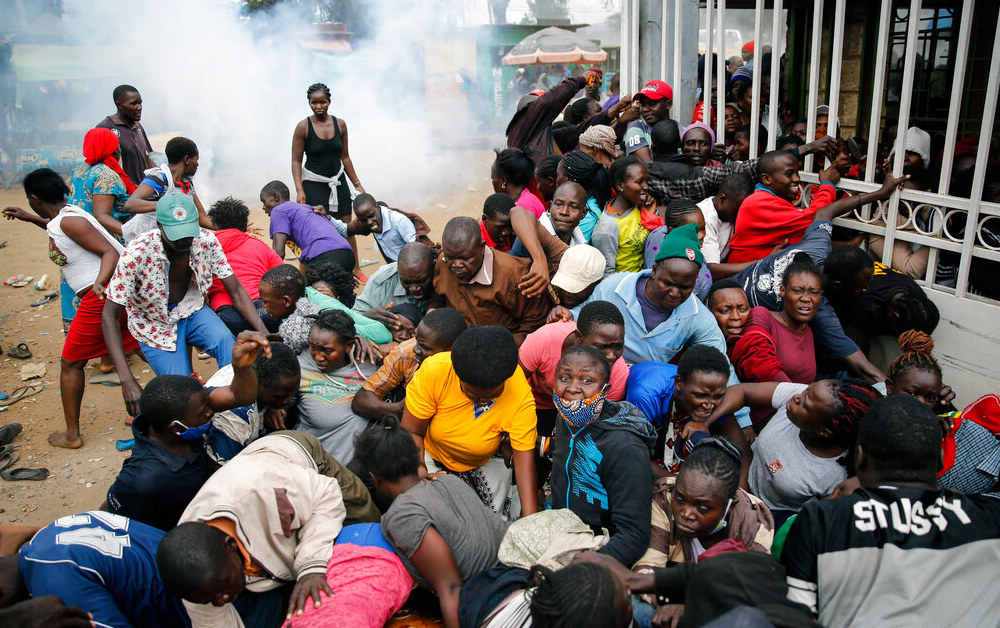In the largest slum in Kenya’s capital, people desperate to eat set off a stampede during a recent giveaway of flour and cooking oil, leaving scores injured and two people dead.
In India, thousands of workers are lining up twice a day for bread and fried vegetables to keep hunger at bay.
Across Colombia, poor households are hanging red clothing and flags from their windows and balconies as a sign that they are hungry.
“We don’t have any money, and now we need to survive,” said Pauline Karushi, who lost her job at a jewellery business in Nairobi and lives in two rooms with her child and four other relatives. “That means not eating much.”
The coronavirus pandemic has brought hunger to millions of people around the world. National lockdowns and social-distancing measures are drying up work and incomes, and are likely to disrupt agricultural production and supply routes — leaving millions to worry how they will get enough to eat.
The coronavirus has sometimes been called an equaliser because it has sickened both rich and poor, but when it comes to food, the commonality ends. It is poor people, including large segments of poorer nations, who are now going hungry and facing the prospect of starving.
“The coronavirus has been anything but a great equaliser,” said Asha Jaffar, a volunteer who brought food to families in the Nairobi slum of Kibera after the fatal stampede. “It’s been the great revealer, pulling the curtain back on the class divide and exposing how deeply unequal this country is.”
Already, 135 million people had been facing acute food shortages but now with the pandemic, 130 million more could go hungry in 2020, said Arif Husain, chief economist at the World Food Programme, a United Nations agency. Altogether, an estimated 265 million people could be pushed to the brink of starvation by year’s end.
“We’ve never seen anything like this before,” Husain said. “It wasn’t a pretty picture to begin with, but this makes it truly unprecedented and uncharted territory.”
The world has experienced severe hunger crises before, but those were regional and caused by one factor or another — extreme weather, economic downturns, wars or political instability.
This hunger crisis, analysts say, is global and caused by a multitude of factors linked to the coronavirus pandemic and the ensuing interruption of the economic order: the sudden loss in income for countless millions who were already living hand-to-mouth; the collapse in oil prices; widespread shortages of hard currency from tourism drying up; overseas workers not having earnings to send home; and ongoing problems like climate change, violence, population dislocations and humanitarian disasters.
Already, from Honduras to South Africa to India, protests and looting have broken out amid frustrations from lockdowns and worries about hunger. With classes shut down, over 368 million children have lost the nutritious meals and snacks they normally receive in school.
There is no shortage of food globally, or mass starvation from the pandemic -- yet. But logistical problems in planting, harvesting and transporting food will leave poor countries exposed in the coming months, especially those reliant on imports, said Johan Swinnen, director-general of the International Food Policy Research Institute in Washington.
While the system of food distribution and retailing in rich nations is organised and automated, he said, systems in developing countries are “labour intensive”, making “these supply chains much more vulnerable to Covid-19 and social-distancing regulations”.
Uncertainty over food is also building in India, where daily-wage workers with little or no social safety net face a future where hunger is a more immediate threat than the virus.
As wages have dried up, half a million people are estimated to have left cities to walk home, setting off the nation’s “largest mass migration since Independence”, said Amitabh Behar, the chief executive of Oxfam India.
On a recent evening, hundreds of migrant workers, who have been stuck in New Delhi after a lockdown was imposed in March with little warning, sat under the shade of a bridge waiting for food to arrive. The Delhi government has set up soup kitchens, yet workers like Nihal Singh go hungry as the throngs at these centres have increased in recent days.
“Instead of coronavirus, the hunger will kill us,” said Singh, who was hoping to eat his first meal in a day. Migrants waiting in food lines have fought each other over a plate of rice and lentils.
Singh said he was ashamed to beg for food but had no other option. “The lockdown has trampled on our dignity,” he said.
Even if there is no major surge in food prices, the food security situation for poor people is likely to deteriorate significantly worldwide. This is especially true for economies like Sudan and Zimbabwe that were struggling before the outbreak, or those like Iran that have increasingly used oil revenues to finance critical goods like food and medicine.
In Venezuela, the pandemic could deal a devastating blow to millions already living in the world’s largest economic collapse outside wartime.
Refugees and people living in conflict zones are likely to be hit the hardest.
The curfews and restrictions on movement are already devastating the meagre incomes of displaced people in Uganda and Ethiopia, the delivery of seeds and farming tools in South Sudan and the distribution of food aid in the Central African Republic. Containment measures in Niger, which hosts almost 60,000 refugees fleeing conflict in Mali, have led to surges in the pricing of food, according to the International Rescue Committee.