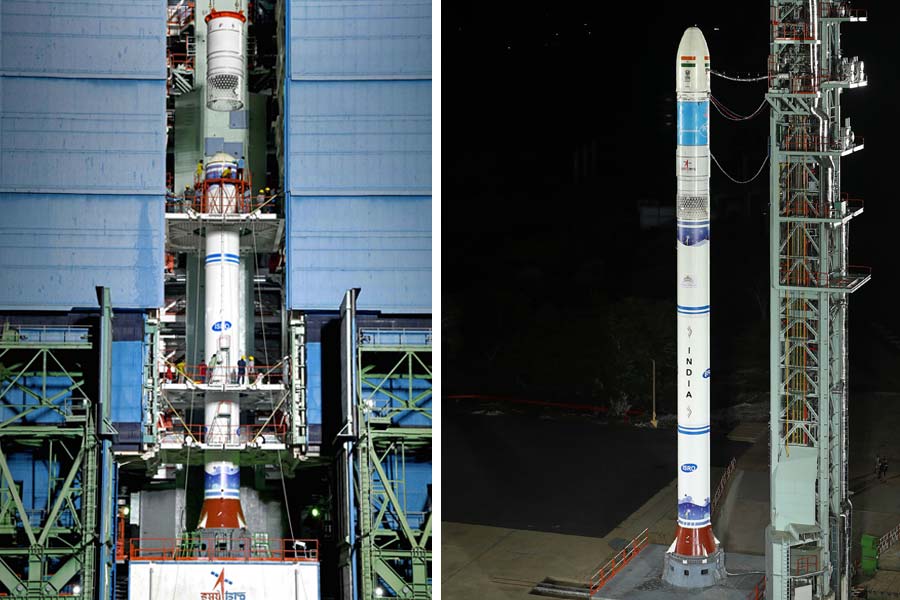
ISRO on Friday launched its third and final developmental flight, Small Satellite Launch Vehicle-D3, carrying Earth Observation Satellite EOS-08.
The rocket lifted off majestically from the first launch pad at the Satish Dhawan Space Centre here, situated about 135 km east of Chennai at a pre-fixed time of 9.17 am.
The objectives of the SSLV-D3-EOS-08 mission include designing and developing a microsatellite and creating payload instruments compatible with the microsatellite bus, the Bengaluru-headquartered national space agency said.
Built on the Microsat/IMS-1 bus, EOS-08 carries three payloads--Electro Optical Infrared Payload (EOIR), Global Navigation Satellite System-Reflectometry payload (GNSS-R) and SiC UV Dosimeter.
The EOIR payload is designed to capture images in the Mid-Wave IR (MIR) and Long-Wave IR (LWIR) bands, both during the day and night, for applications such as satellite-based surveillance, disaster monitoring, environmental monitoring, fire detection, volcanic activity observation and industrial and power plant disaster monitoring.
The GNSS-R payload demonstrates the capability of using GNSS-R-based remote sensing for applications such as ocean surface wind analysis, soil moisture assessment, cryosphere studies over the Himalayan region, flood detection, and inland waterbody detection.
The SiC UV Dosimeter monitors UV irradiance at the viewport of the Crew Module in the Gaganyaan Mission and serves as a high-dose alarm sensor for gamma radiation.
Except for the headline, this story has not been edited by The Telegraph Online staff and has been published from a syndicated feed.