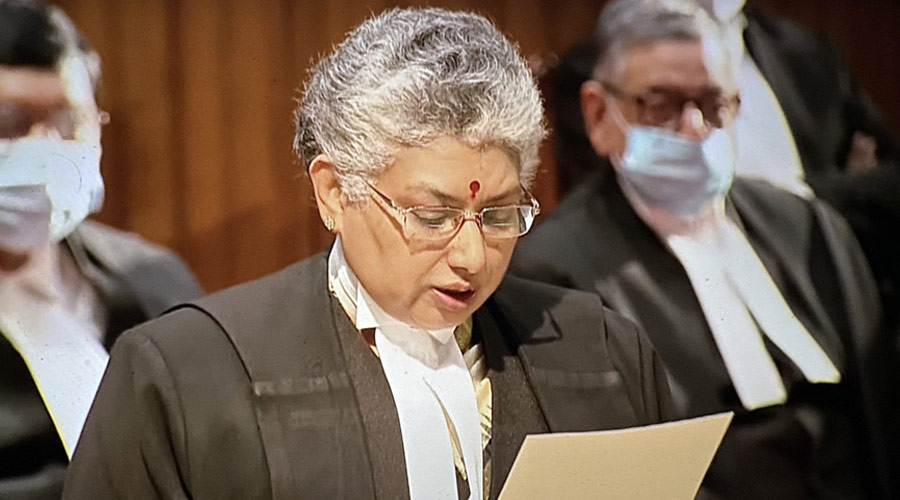
A hate speech strikes at the foundational values of our Constitution, Supreme Court judge Justice B V Nagarathna said on Tuesday and held that such statements can be vicariously attributed to the government in case a minister makes disparaging statements in his "official capacity".
A Constitution bench of Justices S A Nazeer, B R Gavai, A S Bopanna and V Ramasubramanian, in a separate judgement, ruled that a minister's statement cannot be attributed "vicariously" to the government.
Writing a judgement expressing dissent on this issue, Justice Nagarathna said indiscreet speech is a cause of concern in the recent times as it is hurtful and insulting.
"Hate speech strikes at foundation values of the constitution by marking society as unequal. It also violates the fraternity of citizens from diverse backgrounds. The sine qua non (essential condition) of a cohesive society is based on plurality and multi-culturalism such as India that is 'Bharat'. Fraternity is based on the idea that citizens have reciprocal responsibilities towards one another," she said.
Public functionaries and other persons of influence including celebrities are duty bound to be more responsible and restrained in their speech, Justice Nagarathna said.
"They are required to understand and measure their words having regard to the likely consequences on public sentiment and behaviour and also be aware of of the example they are setting on the fellow citizens to follow," she said.
Justice Nagarathna said it is for the party to control the speeches made by their ministers which can be done by forming a code of conduct.
"Any citizen who feels attacked by such speeches made or hate speech by public functionary etc can approach court for civil remedies. It is for parliament in its wisdom to enact a law to restrain public functionary from making disparaging remarks against fellow citizens bearing in mind Articles 19(1)(a) and 19(2)," she said.
The top court judge said for a country like ours which is a parliamentary democracy, freedom of speech and expression is a necessary right for ensuring a healthy democracy.
The court was hearing a plea filed by a man whose wife and daughter were allegedly gang-raped in July 2016 on a highway near Bulandshahr. He was seeking transfer of the case to Delhi and lodging of an FIR against then Uttar Pradesh minister Azam Khan for his controversial statement that the gang-rape case was a "political conspiracy".
The judgement came on a question whether restrictions can be imposed on a public functionary's right to freedom of speech and expression.
Except for the headline, this story has not been edited by The Telegraph Online staff and has been published from a syndicated feed.