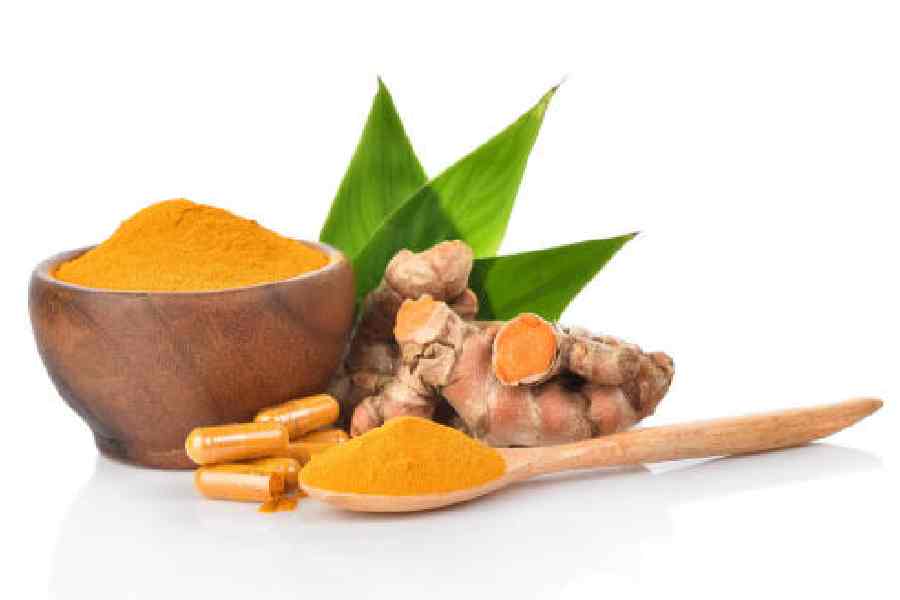
Turmeric has been used as a spice and as medicine for thousands of years. And in recent years, it’s become popular as a dietary supplement in the West where it is often sold as curcumin — a chemical compound found in dried turmeric. There are claims that it can soothe joint pain, reduce inflammation and improve mobility.
In Thailand, turmeric is often consumed in its spice or supplement form to quell gastrointestinal symptoms such as bloating and indigestion, said Dr Krit Pongpirul, an associate professor of preventive and social medicine at Chulalong korn University in Bangkok. But only a few small studies have evaluated such benefits.
In a trial published recently in the journal BMJ Evidence-Based Medicine, Dr Pongpirul and his colleagues tested whether curcumin supplements could help patients with functional dyspepsia, a common gastrointestinal condition that causes stomach pain and feelings of fullness, nausea and bloating after meals.
For the eight-week trial, the researchers split 206 people with functional dyspepsia into three randomly assigned groups: one that took 20 milligrams of omeprazole (a medication that reduces stomach acid) once a day; another that took two 250mg capsules of curcumin four times a day; and a third that took both omeprazole and curcumin in the above doses each day.
There were 151 patients who completed the study, and at four and eight weeks, all three groups reported similar reductions in symptoms such as pain, belching, heartburn and bloating.
According to Dr Pongpirul, the curcumin seemed to be just as effective at reducing symptoms of functional dyspepsia as the omeprazole. Few side effects were reported, although the authors noted that longer term studies were needed to assess the supplement’s risks and benefits.
Dr Brian Lacy, a gastroenterologist and professor of medicine at the Mayo Clinic
in Jacksonville in Florida in the US, said via email that despite these promising results, he would hesitate to recommend curcumin supplements to his patients based on this study alone.
The results would have been more convincing if the study had included a placebo group, he said. Without one, it’s impossible to know if the participants’ responses were from the treatment, from a placebo effect or from the passing of time.
That said, functional dyspepsia causes serious discomfort, Dr Lacy said, and in the US, there are no medications approved to treat the condition. Omeprazole, which is commonly used off-label, seems to help only about one in 10 patients. Without better treatments, Dr Lacy said, those who prefer natural or herbal products “could confidently use this data to say, ‘Let’s try curcumin first.’”
But Mahtab Jafari, a professor of pharmaceutical sciences at the University of California in Irvine, US, cautioned that patients with painful gastrointestinal symptoms should not use curcumin without a medical evaluation. And because dietary supplements are poorly regulated, there are some important caveats that have to be kept in mind.
Turmeric and curcumin are among the most studied dietary supplements, said Dr Janet Funk, a professor of medicine at the University of Arizona in Tucson, US.
In a sweeping review published in March, Dr Funk and her colleagues evaluated 389 clinical trials on how curcumin supplements may influence various health conditions, including type 2 diabetes, osteoarthritis, digestive conditions, cancer and dementia.
Many were small studies and were not well designed, she said, but the evidence did suggest that the supplements were probably helpful for osteoarthritis and potentially helpful for people with insulin resistance or diabetes.
The composition of the products used in those studies varied widely — and so do the supplements currently on the market. That makes it difficult to take promising results for a supplement in a trial and find one in a store to match it.
Curcumin supplements have also been found to have some potentially harmful contaminants. In one study published in 2018, Dr Funk and her colleagues analysed 35 curcumin supplements and found traces of lead in all but one product.
They also found residues of toxic industrial solvents — such as toluene, a chemical found in paint, nail polish and gasoline — in 25 of the products tested, although the solvent levels were below limits generally believed to be safe. And many of the curcumin supplements included piperine, an extract of black pepper, which increases the absorption of curcumin but can also interfere with some medications.
Jafari, who studies curcumin in her own lab, said she is confident that it has real anti-inflammatory effects, but given the lack of large, well designed trials and industry regulation, she does not recommend curcumin supplements.
Before using any dietary supplement, check with your healthcare provider for possible interactions with medications or interference with tests you might need; and continue to monitor yourself for any side effects of taking the supplement, she said.
But given the concerns about purity and safety of turmeric supplements, the best use of the plant might be its oldest: “Buy the beautiful turmeric roots, grind them up, put them in your food and enjoy it,” Jafari said.
NYTNS